Do you know that...
Your sense of smell CAN take you back in time?
Your joints CAN predict the weather?
Your pupils CAN reveal when you are in love?
CAN
It is used to talk about present ability. e.g. ‘I can ride a bike’.
It is used to talk about present possibility. e.g. ‘Can you meet me at 5?’
It is used to make informal requests and orders. e.g. ‘Can you bring me my jumper?’
It has two negative forms, CAN´T and CANNOT.
CAN has not got TO infinitive, Gerund or Past Participle. In all these cases, we use BE ABLE TO
COULD
Is used to talk about past abilities. e.g. ‘When I was a child I could do handstands’.
It used to tal about past possibility e.g. I couldn´t phone you last night/ Could you phone Peter last night?
Is used to make formal requests. e.g. ‘Could you fax me that document by Tuesday?’
In the negative form, is COULDN´T
BE ABLE TO
It can be used instead of CAN and COULD with all tenses. e.g. "I will be able to see you next week".
It is used for Future Simple tense of CAN. e.g. "If I get I job soon, I will be able to buy a new car"
WAS/WERE ABLE TO is used for ability in a specific situation in the past
"I was able to do the crossword in 2 minuites"
PRONUNCIATION OF CAN and CAN´T
The difference between CAN and CAN'T is not the T, because the T usually disappears in a normal conversation. The most important thing to know if it's affirmative or negative is not the T, it is the vowel:
CAN We don't pronounce the vowel, so it sounds /kn/
We don't pronounce the vowel, so it sounds /kn/
CAN'T We don't pronounce the final T, but we pronounce the vowel in the middle strong and clear. Standard British English pronounces this with the vowel in CAR
We don't pronounce the final T, but we pronounce the vowel in the middle strong and clear. Standard British English pronounces this with the vowel in CAR 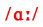
American English pronounces this with the vowel in CAT 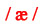
You can find the difference in pronunciation between CAN and CAN´T in this famous song by the Beatles.
















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario